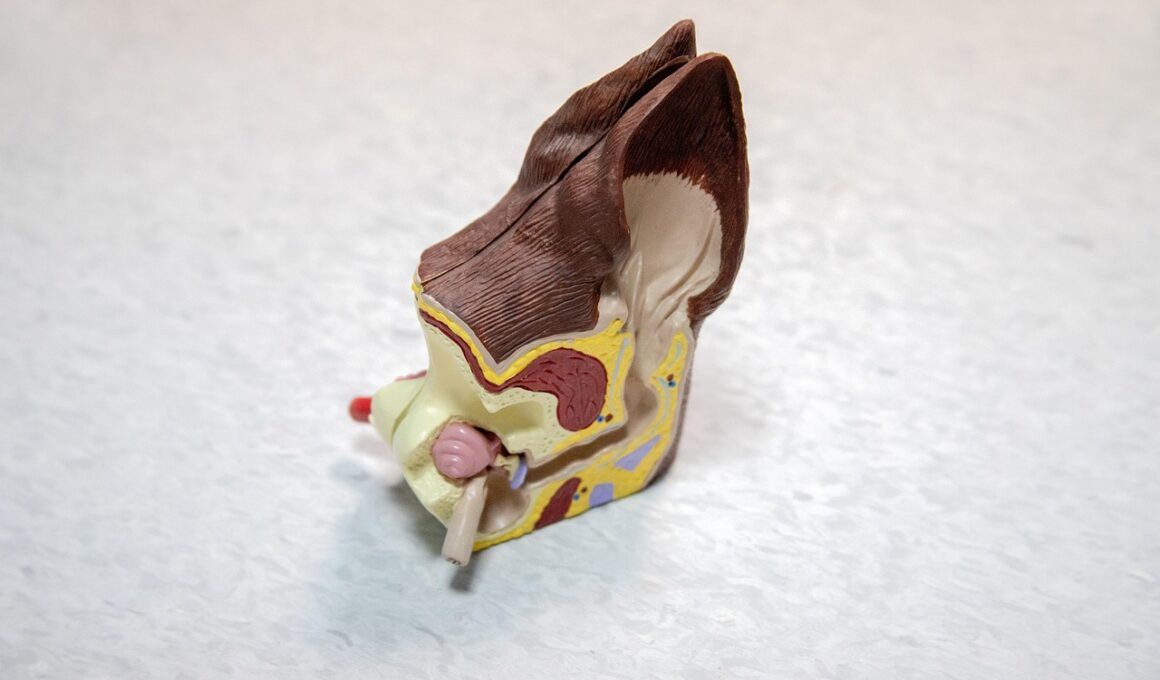
Ear Infection Symptoms and When to Start Treatment
Understanding ear infection symptoms is crucial for early diagnosis and treatment. Ear infections, often prevalent in children, may display a range of symptoms that can affect their daily activities. Common signs include some pain or discomfort in the ear, which may worsen when lying down. Hearing loss is another indicator, often temporary, but noticeable in some situations. You might also observe fluid drainage from the ear, sometimes with a foul odor. Fever can accompany these symptoms, particularly in younger children, highlighting a possible infection. Additionally, irritability and difficulty sleeping can reflect the discomfort caused by the infection. In severe cases, persistent ear infections can lead to further complications, so it’s important to take them seriously. There are two types of ear infections: otitis media and otitis externa. Otitis media affects the middle ear while otitis externa, often referred to as swimmer’s ear, affects the outer ear canal. Knowing the signs can help parents and adults respond timely to the problems. If you notice these symptoms in someone, it is advisable to consult a healthcare professional for appropriate management, testing, and treatment options.
Ear infections symptoms can vary based on age and individual factors. In infants, symptoms may be less obvious. They might pull at their ears or exhibit unusual fussiness, especially when feeding or lying down. Older children are usually more vocal about discomfort, pointing or complaining about ear pain. As the infection progresses, children may lose their appetite and develop a general sense of malaise. In adults, symptoms can sometimes be more intense, leading to severe ear pain, pressure sensations, and difficulty hearing. Pain can sometimes radiate to the jaw or teeth, making diagnosis more complex. It’s also essential to keep an eye out for any swelling or changes around the ear area. Additionally, systemic symptoms such as nausea or dizziness can occur as the body responds to the infection. Another red flag to monitor is persistent fever that doesn’t seem to resolve with standard over-the-counter medications. If multiple symptoms occur consistently for more than a few hours, it’s crucial to seek medical help. Early intervention can prevent further complications and ensure the integrity of your ear health, improving recovery time significantly.
Recognizing Severe Symptoms
If you or your child experience severe symptoms related to ear infections, it is imperative to seek immediate medical attention. Symptoms warranting urgent care include persistent, severe ear pain that does not respond to medication, or the presence of significant swelling around the ear. High fever, typically above 102°F (39°C), especially when combined with other symptoms, is another crucial indicator of a serious infection. If there is bleeding or discharge from the ear that is yellow, green, or foul-smelling, this can signal a more severe issue. Hearing loss that continues after other symptoms fade can also be alarming and needs evaluation. Symptoms such as loss of balance, severe dizziness, or tinnitus (ringing in the ears) are rarely seen but require prompt assessments. It’s vital to communicate all symptoms to a healthcare provider. Your descriptions will help them evaluate the severity of the infection, possibly leading to imaging tests like an ENT exam or hearing tests. Never hesitate to act when these symptoms arise; timely treatment can make all the difference in recovery speed and efficacy.
One of the most crucial aspects of managing ear infections is understanding when to start treatment. If mild symptoms are noted, such as slight discomfort and low-grade fever, home care measures may suffice initially. Over-the-counter pain relievers are commonly recommended and can be effective. However, if symptoms persist for more than about 48 hours without improvement, it might be time to reach out to a healthcare provider. Antibiotics are often the next step, but not always necessary for mild cases. The decision hinges on age, symptom severity, and the individual’s medical history. If the patient is an infant or if there’s a recurrent pattern of infections, the doctor may opt for antibiotics sooner. Always keep track of the symptoms’ duration and intensity to assist medical professionals in making an informed decision. In some cases, if complications are frequent or severe, doctors may recommend preventive approaches, such as ear tubes. Understanding these timelines can significantly enhance health management and provide peace of mind during troubling times.
At-home Remedies and Supported Treatments
Implementing at-home remedies can provide relief and comfort during an ear infection. Warm compresses applied to the affected ear can alleviate pain and discomfort. Additionally, over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen are valuable for managing fever and discomfort. It is essential to adhere to package directions for dosage, especially in children. While some herbal remedies are touted for their effectiveness, consider consulting with a healthcare professional before using them, as these can sometimes interact with prescribed medications. Staying hydrated is also crucial. Encourage patients, especially children, to drink plenty of fluids to remain hydrated, promoting faster recovery. However, if symptoms worsen despite home treatments, it is vital to seek professional medical intervention. Essential oils such as tea tree or olive oil may help soothe symptoms but should never replace medical advice. Knowledge of underlying conditions that may contribute can guide treatment. Since ear infections can often recur, maintaining good ear hygiene practices and staying up to date on vaccinations can help reduce the likelihood of future infections.
In the context of ear infections, knowing when to follow up with your healthcare professional post-treatment is essential. If initial treatment was initiated with antibiotics or other medications, a follow-up visit is typically recommended within a week to assess the effectiveness. This is particularly critical if symptoms have not improved or have worsened during treatment. Observing for any new or emerging symptoms post-treatment becomes a key aspect of recovery. Make note of any changes, whether it’s an increase in pain, re-emergence of fever, or changes in hearing. For chronic ear infections or recurring issues, the healthcare provider may suggest more extensive evaluations to rule out anatomical issues, allergies, or other contributing factors. Communication with your healthcare provider about the entire history of ear infections can be beneficial in crafting a tailored treatment plan. It could provide insights into lifestyle changes or preventative measures. Monitoring changes helps in effective identification of any complications that may arise. Consistent follow-ups ensure comprehensive management of ear health and promote well-being.
Preventative Measures for Ear Infections
Committing to preventative measures is a powerful strategy in reducing the incidence of ear infections. Maintaining proper hygiene is essential; regular handwashing can eliminate germs and bacteria that lead to infections. Additionally, ensuring that children are kept up to date with their vaccinations, such as the pneumococcal and influenza vaccines, can significantly lower their risk. Breastfeeding infants for at least six months has also been shown to provide protection against ear infections, as it helps strengthen their immune system. Practicing good ear care, such as avoiding exposure to smoke, can diminish risk. Parents should also keep an eye on swimming habits and techniques, ensuring children practice proper ear drying methods post-swim to avoid moisture accumulation. Furthermore, utilizing earplugs while swimming can aid in preventing swimmer’s ear, particularly in prone individuals. In homes, maintaining a smoke-free environment is critical. Considering seasonal changes and ensuring proper ventilation also aid in respiratory health. Avoiding allergies causing irritants is always advisable, as these complications can perpetuate ear issues. By implementing these preventive measures, families can work towards maintaining ear health for all members.
Overall, understanding the signs and symptoms of ear infections promotes proactive health management. This knowledge empowers individuals to ascertain when to seek medical attention effectively. Early recognition of symptoms leads to timely interventions, reducing the risk of complications that prolonged infections can cause. Both non-invasive treatments at home and professional medical care play pivotal roles in safe and effective recovery from ear infections. The importance of communication between patients and healthcare providers cannot be overstated; sharing symptoms and treatment responses will lead to better outcomes. Establishing a plan for management will support overall health and help avoid future occurrences. Additionally, educating families about ear health and cultivating healthy practices lays the groundwork for a lifetime of healthy ears. Simple measures, like routine check-ups, remain essential in early detection of potential issues. Emphasizing hygiene, care during swimming, and understanding vaccination approaches can further improve ear health on a broader scale. As we strive to reduce the frequency and severity of ear infections, the collective commitment towards awareness and preventative strategies will yield substantial benefits for future generations.