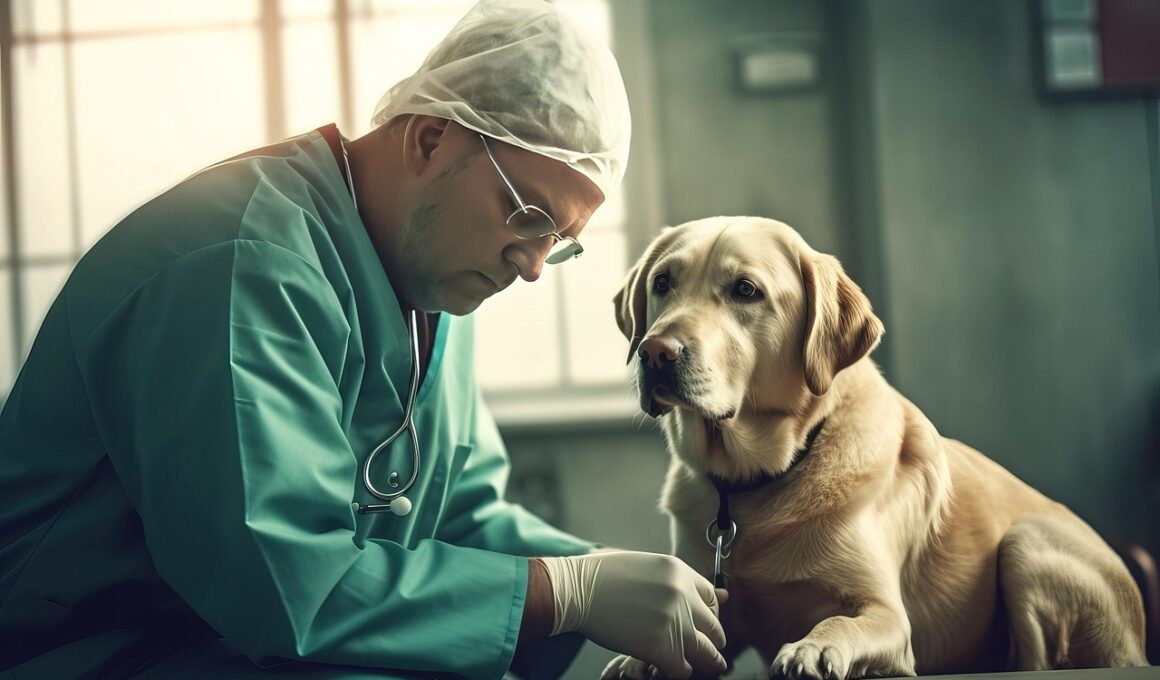
Vaccination Timing and Safety in Dogs and Cats with Autoimmune Diseases
Vaccination in dogs and cats diagnosed with autoimmune diseases is a topic needing thorough attention. Autoimmune diseases can compromise the immune system, posing potential risks during vaccinations. A thorough consultation with a veterinarian allows for the development of personalized vaccination schedules that consider the specific health conditions of these pets. For instance, pets with conditions such as lupus or certain types of cancers must be closely monitored. The use of modified-live virus vaccines can sometimes provoke adverse responses in these animals. Therefore, understanding the types of vaccines recommended for those with immune compromise is essential. It is crucial to distinguish between core vaccinations, which are necessary for public health and the pet’s well-being, and non-core vaccines, which may be optional. A veterinarian will often recommend core vaccines like rabies and distemper for all pets. On the other hand, non-core vaccines, such as for Bordetella or Lyme disease, may be considered on a case-by-case basis. Sensitivity to vaccine ingredients should also be assessed, as some animals may have heightened reactions based on their medical history.
It is important to recognize the timing of vaccinations for dogs and cats with autoimmune diseases. Timing can significantly influence the safety and efficacy of vaccines in these animals. For pets in active treatment for their diseases, such as immunosuppressive therapies, veterinarians usually suggest delaying vaccinations until the pet’s health stabilizes. This pause is crucial as live vaccines might lead to disease exacerbation. Similarly, timing may vary for booster shots; the conventional schedules may not always apply to these special populations. Therefore, adhering to a customized vaccination plan tailored for the individual pet’s health condition is vital. The veterinarian may also recommend pre-vaccine blood tests to check the pet’s immune response to previous vaccinations. Identifying specific antibody levels can guide the decision regarding additional vaccinations, ensuring the pet’s immune system can adequately respond. Regular health check-ups will also provide insights into how the pet is tolerating their vaccinations. Always ensure that vaccinations are administered in a controlled environment, minimizing the risk of reactions during the appointment.
Types of Vaccines and Recommendations
Understanding the different types of vaccines available can ease decision-making for pet owners with dogs or cats that have autoimmune diseases. Core vaccines, generally recommended for all pets, include rabies, distemper, and parvovirus, as they protect against highly contagious diseases. However, with immunocompromised pets, the timing and choice of these vaccines become critical. Non-core vaccines, such as those for kennel cough or leptospirosis, may not be as essential and generally should be given after assessing risks. In certain circumstances, vaccines may be administered in a more diluted form to lessen the potential side effects. The decision to use adjuvanted versus non-adjuvanted vaccines can also be significant; the latter might produce fewer reactions. Discussing with your veterinarian about the specific vaccine brands and the components can help ensure that any vaccine chosen is suitable for your pet’s condition. Additionally, discussing the role of titers as an alternative method for determining immunity could be beneficial. This helps avoid unnecessary vaccinations while ensuring your animal remains protected against infectious diseases.
Pet owners should always monitor their pets closely following vaccinations, especially those with underlying health issues. Potential negative reactions can include fever, lethargy, and, in rare cases, severe allergic responses. It is advisable to watch for signs of swelling or pain at the injection site, as this may indicate an adverse reaction. Developing a system of reporting any changes in health immediately after vaccination is key for these pets. A trusted veterinary practice may provide clear guidelines on what signs to monitor. Documenting symptoms has the added benefit of assisting veterinarians in understanding how each specific vaccine impacts different populations. Providing this feedback can also contribute to improving vaccination guidelines for pets with similar diseases. Regular updates to your veterinarian about your pet’s overall well-being will support adjustments to any vaccination schedule as needed. The collaboration between pet owners and veterinarians is essential in navigating the complexities associated with vaccinating animals with autoimmune disorders.
Establishing a Communication Plan
Establishing a clear communication plan between pet owners and veterinarians is critical for achieving the best vaccination outcomes. Discussing concerns about timing, vaccine choice, and potential side effects should be a routine part of any appointment. Pet owners are encouraged to ask questions and ensure thorough discussion allows for informed choices. Scheduling follow-up consultations after vaccinations can provide opportunities for addressing any concerns about the pet’s reactions or health concerns. By actively participating in your pet’s health, owners foster a proactive approach. Utilizing tools such as a pet health app can be beneficial for tracking vaccination records and appointments. It can also store health history information which may be particularly useful during veterinary visits. Furthermore, sharing any updates with the vet regarding the pet’s condition or changes in their behavior will help the veterinarian tailor future care more effectively. Engaging in discussions about research or guidelines relevant to your pet’s condition can also lead to significant insights on vaccines that work best for them.
Special consideration should also be given to the environment in which the vaccines are administered. Vaccinating pets with autoimmune diseases in low-stress settings can reduce potential anxiety, which may impact overall health responses. Fear and anxiety can exacerbate any adverse reactions they may face. Therefore, a quiet, calm environment is preferable for administering vaccines. Additionally, providing supportive strategies, such as familiar items or comforting toys, can aid in easing the pet’s stress levels. Following vaccination, pets are often observed for a period to ensure they do not exhibit adverse effects. Owners should communicate any discomfort observed during this period to facilitate appropriate interventions. It’s also worth noting that some clinics offer home vaccination services, which can be considered for pets that are particularly anxious about veterinary visits. Ultimately, taking comprehensive steps to ensure a comfortable and supportive environment is essential when vaccinating pets with autoimmune diseases, as their well-being is paramount during this process.
Conclusion
In conclusion, vaccinating dogs and cats with autoimmune diseases requires a tailored approach, ensuring their safety and health. Consultation with a veterinarian is indispensable for creating individualized vaccination plans. Regular assessments and open communication with your vet can lead to a successful vaccination strategy that aligns with your pet’s unique health needs. It is also important to stay informed about any new guidelines or research concerning vaccinations in animals with compromised immune systems. In many cases, owners may find a balance between achieving sufficient immunity and minimizing risks. Being proactive about health check-ups and vaccinations allows for better outcomes in these special populations. As such, taking preventative measures through proper vaccinations can contribute greatly to the long-term health and quality of life of pets with autoimmune diseases. Understanding the complexities related to vaccinations will empower pet owners in making informed choices. By prioritizing your pet’s health, you can navigate the challenges associated with vaccinations confidently, protecting them from communicable diseases while safeguarding their immune systems efficiently.
Utilizing the latest research and veterinary practices will enhance the safety and timing of vaccinations for dogs and cats fighting autoimmune diseases. Various veterinary organizations publish recommendations which can serve as excellent resources in this pursuit. Regular veterinary check-ups will fortify the pet-owner bond, leading to precise and informed decision-making. This comprehensive vaccination approach ultimately benefits pets and develops a deeper understanding of autoimmunity dynamics.