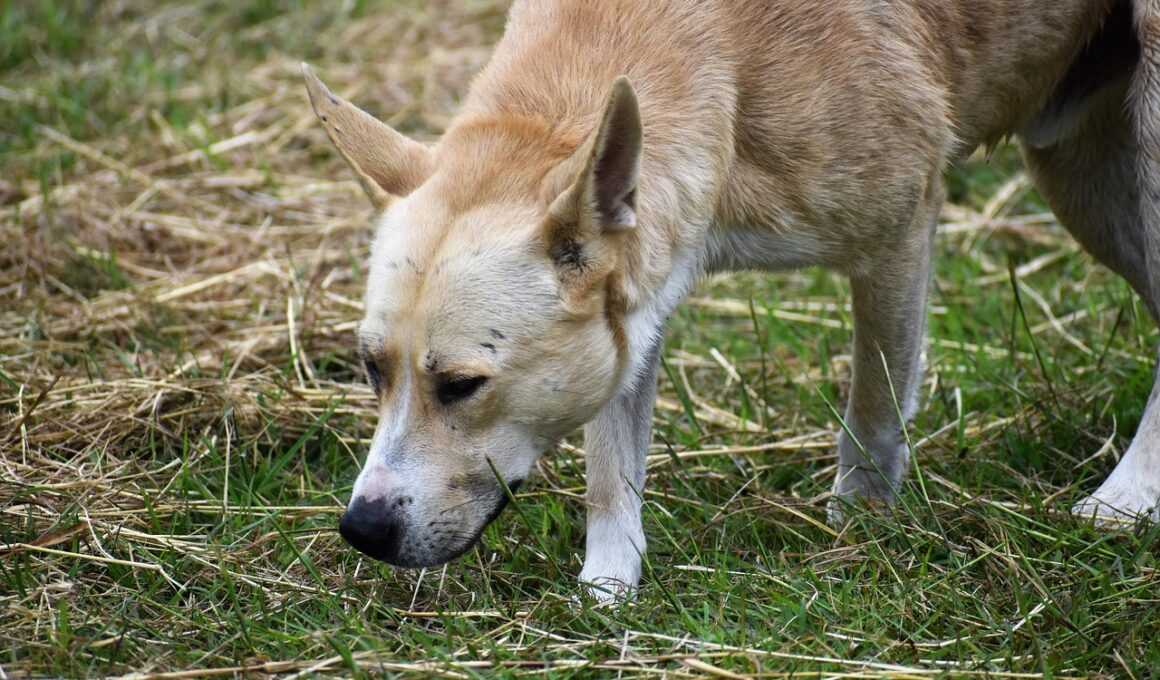
The Science of Tracking: Dogs’ Use of Scent in Search and Rescue
Dogs possess an extraordinary ability to detect scents, making them invaluable assets in search and rescue missions. Their sense of smell is significantly more advanced than that of humans; in fact, studies suggest that a dog’s olfactory receptors are about forty times more sensitive. When a dog is deployed for search and rescue, it can identify specific scents that humans cannot. This innate ability allows them to track missing persons, locate disaster survivors, and even detect specific substances such as explosives or narcotics. The training process for a search-and-rescue dog involves not only scent recognition but also behavioral conditioning. Dogs learn to associate particular scents with rewards, which encourages them to actively seek out those scents in practical scenarios. Whether they are searching for a lost hiker in a forest or a child in an urban setting, dogs utilize their finely tuned senses to locate individuals effectively. Their tracking methods are based on scent molecules left behind, which may include skin cells, clothing fibers, and other personal items. This fascinating process highlights the remarkable capabilities of dogs and their roles in emergency response activities.
Understanding how dogs track scents involves examining the biological functions that contribute to this skill. Dogs have over 300 million olfactory receptors in their noses compared to about six million in humans. This allows canines to differentiate scents in a way that is both sophisticated and nuanced; they can even distinguish between the scents of different people. The training these dogs undergo prepares them for the challenges they will face in real-world scenarios, including various terrains and weather conditions. Factors such as wind direction and humidity can significantly affect scent dispersal, and dogs are trained to adapt their techniques accordingly. Furthermore, dogs also utilize a behavioral technique known as ‘scent discrimination,’ enabling them to focus on a specific scent while disregarding other smells. This skill is critical during missions where multiple scents may overwhelm them. When a rescue dog locates a source of the scent, it signals its handler by implementing a trained behavior, such as sitting or staying. This clear communication shows the bond and understanding between the dog and its handler in high-stress situations, proving vital for successful rescues, often saving lives through their exceptional abilities.
The Importance of Trust Between Dog and Handler
Building a solid relationship between a rescue dog and its handler is crucial in search and rescue operations. Trust fosters communication, which is essential when a dog identifies a scent during intense conditions. Handlers must train diligently to understand their dog’s cues, as this communication can occur under challenging circumstances. A handler’s ability to recognize the signals given by their canine counterpart can make all the difference in swiftly locating an individual. Without trust, dogs might hesitate, or exhibit lack of confidence in their instincts during critical moments. The partnership must be cultivated through consistent joint training exercises that allow dogs and handlers to develop symbolic understandings of each other’s capabilities. These exercises often include practice scenarios where dogs must locate an object or person hidden from sight, mimicking real emergency situations. This trust translates into higher efficiency during actual search and rescue missions. Moreover, dogs trained in rescue work often display a keen enjoyment for their job, which can be a motivating factor in performing tasks effectively. The bond, built on mutual respect and encouragement, can lead to rapidly successful operations that reinforce the effectiveness of professional search and rescue teams.
The versatility of dogs in search and rescue roles is remarkable, allowing them to perform various specific functions based on the needs of the mission. Some dogs are trained for air scenting, meaning they can detect scents carried on the wind from considerable distances, making them ideal for vast outdoor settings. Others specialize in tracking, which involves following a specific scent trail left by the individual. Even within these categories, each dog can be trained for specific types of search tasks. For example, certain breeds excel in mountainous terrain, while others might be more adept in urban environments. The diversity of breeds and their capabilities can significantly enhance rescue operations. While the Labrador Retriever and German Shepherd are popular breeds in this field, other dogs like Bloodhounds possess an unparalleled ability to trail by scent. Their commitment to maintaining focus on the task at hand sets them apart from other trained animals. Additionally, search and rescue dogs are often cross-trained in various disciplines, enabling them to shift from one role to another, which helps agencies maximize their resources effectively during emergencies, demonstrating their adaptability in varying scenarios and conditions.
Health Considerations for Search and Rescue Dogs
Aside from the intensive training search and rescue dogs undergo, their physical health, and mental well-being is of utmost importance in maintaining their effectiveness. Regular health check-ups are necessary to ensure that these canines remain fit and robust, particularly given the strenuous demands of their work. Elements such as proper nutrition, exercise routines, and mental stimulation play significant roles in enhancing their physical abilities. Search and rescue missions often take place in extreme weather conditions, requiring dogs to endure diverse environmental challenges. Handler and owner responsibilities include providing adequate hydration and protective gear in harsh climates. Mental fatigue can also become a concern after extended missions, as dogs may experience stress through sustained work effort. Therefore, introducing playtime, rest periods, and recreational activities is vital to keeping search dogs engaged and less susceptible to burnout. Furthermore, regular vet visits and monitoring ensure that any underlying health concerns are identified promptly to prevent issues from compounding. The overall well-being of these dogs greatly influences their operational performance, emphasizing the importance of responsible care in supporting their capacities, and ultimately fostering successful rescue missions that save lives.
Collaboration across multiple organizations enhances the effectiveness of search-and-rescue teams, showcasing the importance of partnerships in disaster response. Various agencies, including local law enforcement, fire departments, and emergency medical service providers often come together to form coordinated search efforts during crises. Synchronization among these teams is enhanced when canine units are incorporated into the fold, facilitating specialized capabilities that human responders cannot typically achieve alone. Integration of K9 teams allows for a systematic approach when searching for lost individuals, as dogs can cover vast areas efficiently, streamlining the overall operation. Each team member contributes unique skills, ensuring a comprehensive search strategy that accounts for experience levels and training backgrounds. Additionally, cross-training sessions between different agencies often take place, promoting shared knowledge and the establishment of standard operating procedures. This helps to build greater teamwork sensibilities, which can be incredibly beneficial in high-stress environments of search missions. As agencies work together towards a common goal of ensuring safety, the role of dogs as essential partners cannot be overstated, emphasizing their crucial contribution to successful recoveries in search and rescue scenarios.
Conclusion: The Future of Canine Search and Rescue Teams
As societal needs evolve due to climate change and increased frequency of natural disasters, the role of trained search and rescue dogs will continue to expand. The demand for highly skilled canine teams is increasing, requiring continuous advancements in training and methodologies. Emerging technologies can be incorporated to support and enhance tracking capabilities, while preserving the instinctual traits that make these animals effective. For instance, using GPS trackers or scent tracking devices can facilitate better coordination between handlers and dogs, ensuring efficient mission execution. Additionally, expanded training programs could target the socialization of dogs to ensure adaptability in various environments. By fostering and nurturing these pets, agencies can maximize their effectiveness in challenging scenarios, especially as the complexity of disasters grows. As species evolve, so too must our understanding of canine psychology and capabilities. Maintaining a focus on ethical sourcing and breeding practices will also help advance the well-being of search and rescue dogs. Ongoing research into their capabilities will further enhance our understanding, improving event response times. The future of canine units in search and rescue holds promise, as they exhibit unwavering dedication and partnership in ensuring safety in times of need.
In summary, the incredible ability of dogs to track scents plays a pivotal role in search and rescue operations, showcasing their importance in emergency response efforts. With their unparalleled sense of smell and the trust built between canines and their handlers, these dogs provide a necessary function that can mean the difference between life and death. The training and care involved are extensive, ensuring that they are equipped to face the challenges presented in various environments. Organizations and agencies continue to recognize and invest in canine search and rescue teams, promoting the development of effective partnerships. As the future unfolds, we can anticipate further advancements in training techniques and technology that will bolster these teams. The dedication of the handlers combined with the instinctual abilities of the dogs highlights not only their effectiveness but also the emotional bond that flourishes throughout their working relationship. As more stories emerge about the successes achieved and lives saved, the importance of supporting these groups and celebrating their contributions becomes that much clearer. Understanding and nurturing the psychological needs of these canines will ensure their lasting impact in search and rescue, underscoring the heroism present in both dogs and their dedicated handlers.