Case Studies on Canine Lyme Disease: Symptoms and Treatment
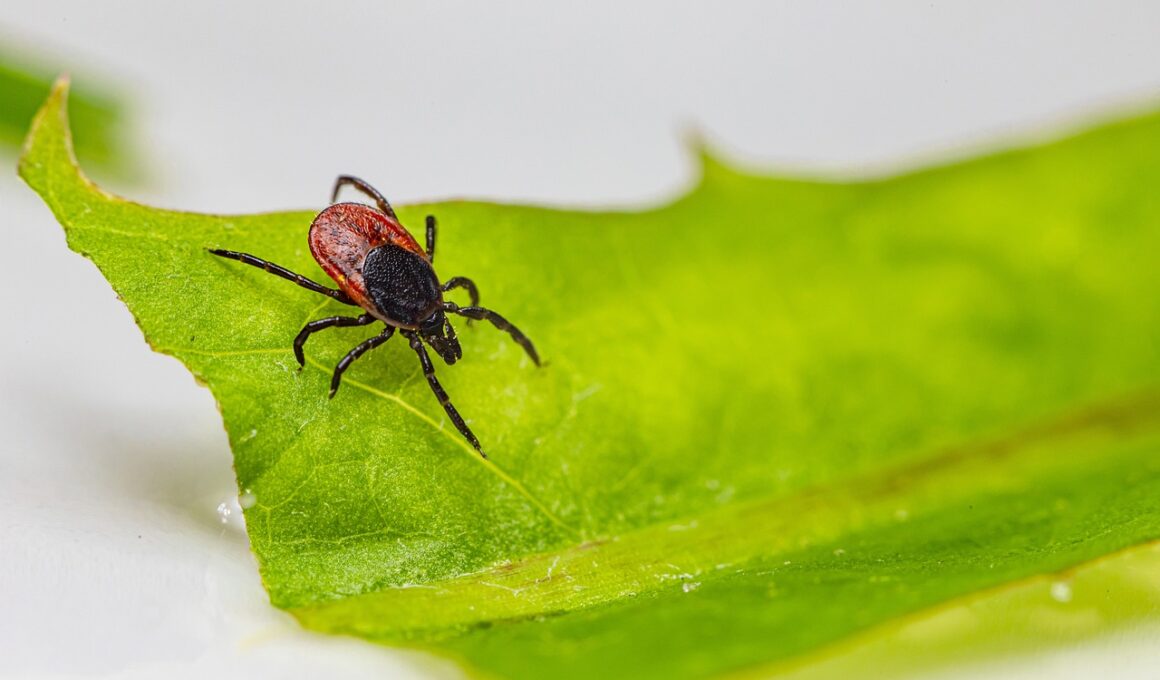
Canine Lyme disease is a significant health concern among pet owners, especially in areas where ticks are prevalent. This infection is caused by the bacterium Borrelia burgdorferi, transmitted through the bite of infected ticks. Symptoms often vary but can include fever, fatigue, diminished appetite, and swollen joints. The condition, if left untreated, can result in more severe issues like joint pain or kidney problems. In this article, we will explore intimate case studies that further illustrate the effects of Lyme disease on dogs, highlighting the symptoms and treatments experienced. Each case will shed light on the importance of early detection and the effectiveness of various treatment options. Canine Lyme disease can be challenging to diagnose as the symptoms initially mimic other health issues. Therefore, it is crucial for dog owners to consult with veterinary professionals upon noticing any signs of illness. Preventative measures such as tick control and routine check-ups play an essential role in keeping dogs safe from the disease. Understanding the symptoms and seeking vet care promptly can make a significant difference in outcomes.
Understanding the Symptoms
The symptoms of Lyme disease in dogs can vary considerably, often making diagnosis quite challenging. In one particular case study, a two-year-old Labrador experienced intermittent lameness that perplexed its owner. Along with joint swelling, the dog appeared lethargic, causing the owner to worry. A visit to the vet revealed elevated levels of antibodies, confirming Lyme disease. It’s important to note that some dogs might show no symptoms at all, while others may experience severe complications. Other common signs include recurrent fever, reluctance to move, and even behavioral changes such as increased irritability. The vet promptly prescribed a course of antibiotics, usually doxycycline, which is effective against this bacterium. Initial treatment often sees a marked improvement in symptoms, typically within two to four days. The dog’s owner was advised to monitor for any additional symptoms and maintain follow-up visits. This case emphasizes the need for dog owners to be vigilant regarding their pet’s health. Since Lyme disease can lead to further complications if left untreated, recognizing symptoms early is crucial for effective management.
In another case, a golden retriever displayed symptoms that progressed rapidly over a few weeks. Initially, persistent stiffness seemed innocuous, but soon the dog was lethargic and avoided walking altogether. Tests confirmed the presence of Lyme antibodies. Interestingly, the owner reported that the dog had been frequently exposed to grassy areas known for ticks. Treatment commenced with antibiotics paired with anti-inflammatory medications to manage pain. This balanced approach was instrumental in the dog’s recovery as it improved mobility significantly. Within two weeks, the retriever was back to its playful self, running around and engaging in regular activities. This case highlights the importance of understanding the continuum of symptoms. If dogs do not receive prompt treatment, they may suffer from chronic conditions that can impact their quality of life. Therefore, proactive strategies such as vaccination and tick prevention become vital components of canine health care. By mitigating exposure to ticks and ensuring regular veterinary consultations, pet owners can reduce the risk of Lyme disease drastically.
Treatment Methods
When it comes to treating canine Lyme disease, a multifaceted approach tends to yield the best results. A case involving an older beagle provides valuable insights into the long-term implications of the disease. The beagle initially exhibited arthritis-like symptoms, causing the owner to think age was the factor. Upon veterinary examination, Lyme disease was diagnosed. The treatment plan included antibiotics and joint supplements tailored for older dogs. This initiated a more comprehensive strategy encompassing routine veterinary check-ups to monitor disease progression. Pain management techniques also included therapies that helped improve joint function, thereby enhancing the dog’s overall well-being. As treatment progressed, the beagle began showing significant improvement with reduced stiffness and increased activity. This case illustrates the necessity of a tailored treatment plan, especially for older dogs who may have multiple health issues. The integration of dietary adjustments and professional monitoring proved beneficial for the beagle’s health regimen. Pet owners must advocate for their pets’ health, understanding that timely intervention and consistent care can lead to a more vibrant and fulfilling life for dogs affected by Lyme disease.
A more extensive case study involved a border collie with recurring bouts of lyme-related symptoms, exacerbated by an underlying autoimmune condition. The complexity of this case demonstrated the unpredictable nature of the disease’s symptoms when combined with pre-existing health issues. After multiple vet consultations, an integrated treatment approach that included traditional antibiotics, immune modulators, and a specialized diet was developed. Regular blood tests monitored both the Lyme disease status and the autoimmune condition, allowing for necessary adjustments to the treatment. Remarkably, as the collar improved in immune function, the Lyme symptoms significantly diminished. The owner mentioned that adopting a holistic view of health not only enhanced their pet’s quality of life but also promoted adherence to preventive measures. This case illustrates how understanding the broader health context surrounding canine Lyme disease can lead to better outcomes. Ensuring comprehensive health care will minimize risks of complications. Each affected dog is unique, necessitating an individualized strategy that takes into account their specific circumstances.
Preventative Measures
Preventative measures offer a pivotal role in managing canine Lyme disease risks. One case study involving a working dog in the field highlights proactive approaches to tick prevention. This dog experienced a tick bite, leading to Lyme disease confirmation. However, vigilant use of tick repellents, consistent grooming, and frequent checks reduced the exposure risk subsequent to the initial episode. This dog and its owner adopted a robust protocol, ensuring preventive canine vaccinations and seasonal accommodations aligned with routine vet visits. Incorporating these practices created an environment fertilized for both education and precaution. As further follow-ups were conducted, it became clear that the comprehensive prevention approach led to significant differences in health outcomes while reducing the recurrence risk of Lyme disease in working conditions. The owner stressed the need for consistent pet safety measures while outdoors. Understanding tick species’ behaviors and locations optimally aids in reducing bite risks. Therefore, implementing these strategies collectively leads to fewer health challenges for your pet, emphasizing that prevention truly is better than cure.
Owning a dog with a history of Lyme disease can be stressful, but it also presents an opportunity for learning. An insightful case study focused on an owner who faced challenges after their dog was diagnosed. Together, they navigated the complexities of treatment, prevention, and symptom monitoring diligently. This experience imparted vital lessons on pet health management, emphasizing regular exercise and a balanced diet to support the dog’s recovery. Daily routine adjustments incorporated fun activities suited to the dog’s recovery stage, minimizing sedentary behaviors. The owner’s commitment, alongside guidance from veterinarians, fostered a strong relationship centered on well-being, care, and understanding. Knowledge about Lyme disease impacts not only the affected canine but also teaches owners about dedication to pet care. This ongoing journey of learning and adapting is crucial for managing ongoing health concerns while fostering resilience in both pets and owners. Recurrent vet visits and open dialogue regarding symptoms empowered the owner’s participation in daily care routines. Most importantly, the owner transformed an initial setback into a platform for ongoing education about Lyme disease.
Conclusion
With continual learning, pet owners can enhance their understanding of canine Lyme disease, its effects, and the essential steps for management. Each case discussed in this article represents varied experiences of owners committed to their pets’ health. Prompt recognition of symptoms, appropriate treatment protocols, preventive measures, and a proactive approach to ongoing care can contribute to significantly improved outcomes. Whether dealing with immediate treatment or longer-term management, vigilant monitoring remains essential for pet health. By sharing these stories and experiences, owners are encouraged to collaborate closely with veterinary professionals to ensure their pets’ well-being. This integrative approach to canine Lyme disease can often lead to hopeful recoveries and integrated health solutions, enhancing the bond between dogs and owners. Going forward, pet owners can cultivate an environment that promotes health, safety, and happiness regardless of past experiences. Each success story serves as inspiration, reminding pet owners that with dedication, they have the power to positively impact their canine companions’ lives, effectively battling Lyme disease as a united front.