Challenges of Negative Reinforcement
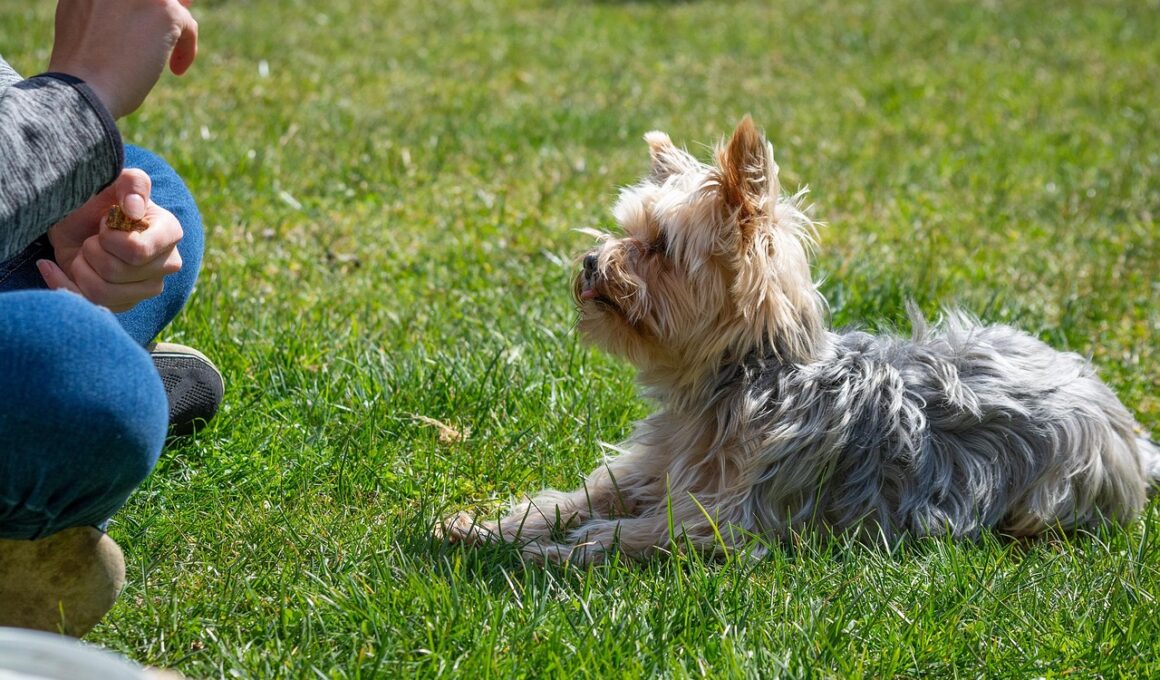
Negative reinforcement in pet training often involves the removal of an unpleasant stimulus following a desired behavior. While this method can effectively modify behavior, it carries distinct challenges that trainers must navigate. One primary challenge is that negative reinforcement can lead to an increase in stress or anxiety in pets. When a pet associates a behavior with discomfort, it can create fear, leading to behavioral issues rather than resolving them. Trainers must be aware of the emotional implications of using negative reinforcement strategies. Another concern is inconsistency in application; using negative reinforcement sporadically can confuse pets and lead to erratic behavior. For example, if a pet receives a command that leads to positive feedback one time and negative feedback the next, it becomes unclear which behavior is desired. Clear signals and consistency in training methods can help overcome these challenges. Moreover, trainers should prioritize communication with the pet, ensuring that pets feel secure and understood during the learning process. It is essential to remember that promoting positive experiences can often yield better long-term results than relying heavily on negative reinforcement techniques.
Another critical issue associated with negative reinforcement is the possibility of developing a negative relationship between the trainer and the pet. When pets perceive training sessions as punishing, they may disengage from the learning process altogether. This disengagement can significantly undermine the effectiveness of training efforts. Instead of establishing a bond built on trust and respect, trainers may find themselves facing resistance. This challenge is particularly acute in young animals, who may not yet have developed coping mechanisms for dealing with discomfort. To counteract this, trainers should engage in practices that emphasize trust-building. For example, incorporating treats or praise after completing a difficult task can help pets associate training with positive experiences. Additionally, positive reinforcement can lead to a more joyful and harmonious learning environment for both the pet and the trainer. Engaging pets in training should be a partnership, where both parties feel respected and valued. By focusing on building a positive rapport, trainers can improve outcomes significantly. Ultimately, trainers must balance methods to ensure they promote learning while avoiding adverse experiences that may stem from negative reinforcement.
Managing Negative Experiences
To effectively utilize negative reinforcement without exacerbating issues, trainers must consider alternative strategies that can complement their training. One valuable tip is to implement gradual exposure to distressing stimuli that help pets adapt over time. For example, when training a fearful dog, exposing them to moderately stressful situations gradually can help build resilience. Pairing exits from distressing scenarios with the desired behavior, such as calmness or obedience, can help reinforce positive outcomes. Understanding the individual pet’s temperament and thresholds is critical in this approach. Training programs should also prioritize creating a safe and secure environment where pets feel comfortable exploring and learning. Additionally, trainers can integrate varying types of positive reinforcement, such as playtime, attention, or treats when the pet successfully performs the desired behavior. By alternating between different approaches, negative experiences can be mitigated without overwhelming the pet. Foster an atmosphere of clear rewards and expectations, enabling pets to thrive while minimizing the potential negative impacts of reinforcement. Ultimately, the goal should be to promote well-rounded, confident behavior by balancing reinforcement approaches effectively.
Knowing when to shift from negative to positive reinforcement is crucial in balancing training methods. As pets demonstrate understanding and begin responding to commands, it provides an excellent opportunity to transition to a more positive framework. This shift can include rewarding desired behaviors consistently with treats or praise and gradually removing negative reinforcements. Trainers must remain attentive during this transitional period, ensuring pets solidify their understanding of commands in an encouraging manner. Insightful trainers recognize that what truly matters is the pet’s emotional wellbeing. Incorporating engagement and excitement into training sessions, rather than relying solely on corrective approaches, can promote a deeper bond. Providing pets with confidence is imperative; it ensures they approach training with enthusiasm and eagerness. Additionally, positive reinforcement often leads to quicker learning and stronger retention of behaviors in the long term. Trainers should create an environment where mistakes are viewed as stepping stones rather than setbacks, fostering resilience in pets. As pets respond positively, confidence will flourish. This confidence ultimately leads to a more reliable and willing companion, transforming negative reinforcement scenarios into opportunities for growth.
Building Trust with Positive Reinforcement
To further mitigate the challenges of negative reinforcement, trainers can focus on building rapport through trust. Trust is vital for effective training; when pets trust their trainers, they are more likely to remain engaged in the learning process. To cultivate this trust, trainers can employ consistent routines that help pets understand expectations and consequences better. Once pets recognize that their actions are rewarded, they may be less prone to confusion or anxiety during training sessions. Additionally, trainers should consider varying reward types to keep training sessions interesting; utilizing games, toys, or social interactions can also foster a sense of enjoyment. Keeping training sessions brief yet impactful ensures that pets remain focused and motivated. Furthermore, using positive reinforcement can dramatically shift a pet’s attitude towards training, leading to increased cooperation and enthusiasm. Taking breaks during intense training sessions can also help maintain a positive atmosphere; ensuring pets have fun and clarity fosters a healthy learning environment. Ultimately, when trainers prioritize the emotional wellbeing of the pet, they can create a foundation for learning that promotes long-lasting, effective behaviors.
Incorporating environmental management strategies helps avoid misuse of negative reinforcement, reducing the likelihood of negative experiences. For example, when introducing pets to new commands, creating a controlled environment free from distractions allows them to focus on the task. During these introductions, relying on rewards ensures that the context remains positive. Allowing pets to progress at their own pace facilitates understanding and builds confidence, preventing feelings of frustration that typically accompany negative reinforcement. Implementing a system of clear signals can greatly enhance communication. Utilizing clicker training, for instance, can provide quick and consistent feedback to pets about the appropriateness of their behavior. Such clarity is essential for fostering positive experiences during training. Planning ahead with structured training sessions can create specific, achievable goals that guide pets towards learning. Proactive trainers emphasize prevention rather than correction, allowing them to sidestep the challenges associated with negative reinforcement. Creating a framework for successful learning experiences strengthens connections between trainers and pets. This collaborative effort leads to consistent positive results and reinforces that making mistakes is part of the learning journey, enhancing overall progress.
Conclusion on Positive Training Techniques
Emphasizing positive reinforcement as the primary method in training not only enhances learning but also safeguards the relationship between pets and trainers. Balancing this approach with strategies for overcoming challenges is vital for ensuring effective pet training. Prioritizing clear communication fosters understanding and builds trust between trainers and pets. An open line of communication allows trainers to adjust their methods based on the pet’s responses continually. It is necessary for trainers to engage pets in a way that highlights their strengths and encourages their development. Developing sessions that sustain motivation and engagement demonstrates the commitment to a positive training experience. With a clear focus on this primary goal, behaviors developed through positive reinforcement are often more natural and long-lasting compared to those gained through primarily negative methods. In conclusion, trainers should aim to create a supportive environment fostering mutual respect and understanding. By prioritizing positive reinforcement techniques and tackling the challenges of negative reinforcement thoughtfully, trainers can achieve better training outcomes, happier pets, and a harmonious relationship that fosters successful learning experiences.