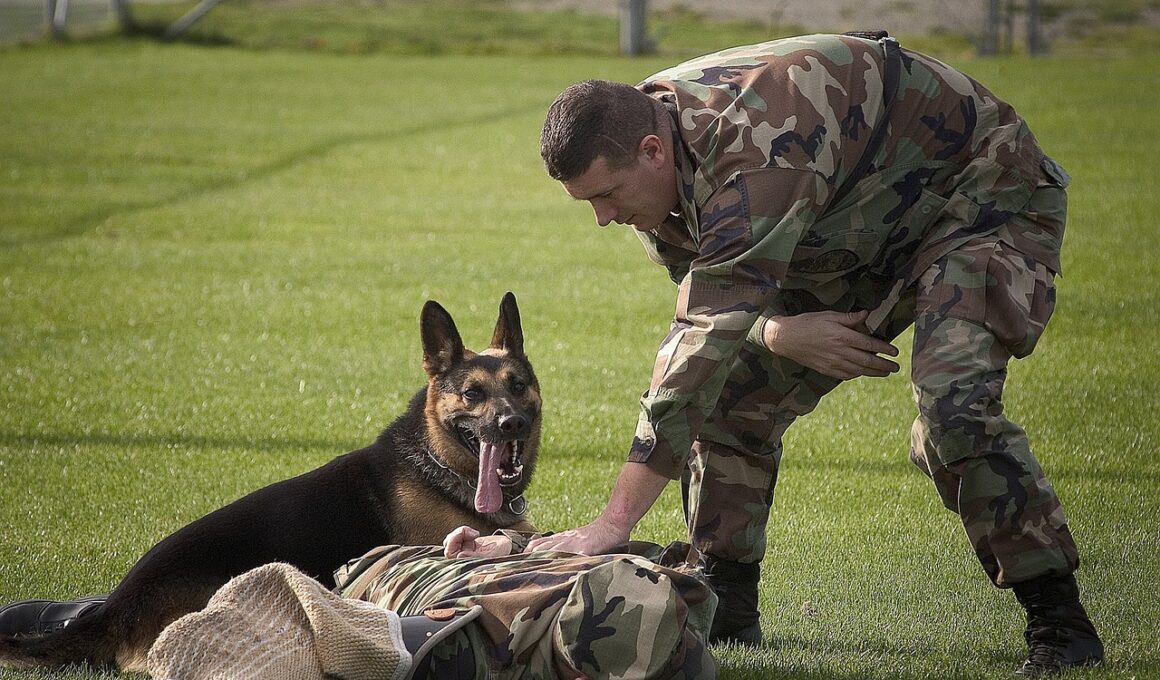
Understanding Agility Training for Military Dogs and Tactical Operations
Agility training for military dogs serves a crucial purpose in enhancing their operational effectiveness. In military contexts, dogs are more than companions; they are integral members of tactical units. Training focuses on building essential skills that allow these dogs to respond quickly in challenging situations. Obstacle courses, for example, are frequently used to develop physical agility and mental sharpness. These courses typically involve jumping, crawling, and navigating through varied terrains. Military dogs are also trained to follow specific commands with precision and to adapt to rapidly evolving scenarios on the field. Consistent training reinforces the bond between the handler and the dog, fostering teamwork. As a result, these dogs can effectively assist in missions such as search and rescue, detection of explosives, and apprehending suspects. Moreover, investing in agility training influences the overall success of military operations by ensuring dogs can operate efficiently under pressure. This training not only assists them in fulfilling their assigned roles but also enhances their safety and that of their handler. Such dynamic training approaches ensure dogs are well-prepared for the unpredictable nature of combat environments.
The importance of physical fitness in agility training for military dogs cannot be understated. Just like human soldiers, these dogs must exhibit peak performance to succeed in challenging situations. Training regimens typically include vigorous exercises to enhance strength, stamina, and cardiovascular health. For example, sprinting, swimming, and weight pulling represent various methods to improve overall physical conditioning. These exercises prepare dogs to undertake demanding tasks, such as pursuing a suspect or navigating difficult terrains. Moreover, agility training integrates endurance runs that build sustained energy levels essential for long missions. Proper nutrition also plays a pivotal role, ensuring that military dogs maintain optimal body condition and muscle recovery. Engaging dogs in variety during training also prevents boredom, keeping them mentally stimulated. Incorporating play and rewards within training sessions fosters motivation and eagerness to learn. Transitioning between different courses and exercises helps dogs remain agile and versatile in varying contexts. This blend of physical workouts with mental challenges not only enhances their agility but also helps them develop a sharp reflex for tactical operations. Thus, a thorough understanding of agility training forms the foundation for the effectiveness of military canines in action.
Techniques and Tools Used in Agility Training
The training environment for military dogs features many specialized tools and techniques designed to optimize their agility training. Various equipment such as jumps, tunnels, and weave poles are utilized to create diverse obstacle courses. These tools help simulate real-world scenarios that dogs may face in active duty. For instance, jumps enhance the dog’s ability to leap over barriers, while tunnels and weave poles improve their coordination and speed. The training process employs clickers or verbal cues to reinforce positive behaviors and successful maneuvers. The concept of positive reinforcement demonstrates remarkable success in training; dogs quickly learn to associate correct actions with rewards. Sessions are usually tailored to each dog’s individual strengths, weaknesses, and learning pace, ensuring a personalized training approach. Each exercise is designed to ensure that both the handler and dog work cohesively, leveraging the canine’s innate instincts alongside learned behaviors. Gradually increasing difficulties as the dog becomes more proficient ensures continuous development and creates a resilient working dog. This structured environment encourages military dogs to push their limits while developing skills crucial in tactical operations. Thus, the implementation of these tools directly impacts the overall agility and effectiveness of military canines.
A critical element of agility training involves the assessment of individual performance and progress throughout the training period. Regular evaluations help handlers identify areas of improvement, providing insight into the dog’s capabilities. Assessments can include measuring speed, accuracy, and response times, with trainers making adjustments based upon each dog’s unique needs. This feedback loop ensures that their training stays on track and continues to challenge them effectively. Handlers often utilize video analysis to review performance, facilitating constructive critiques for further enhancement. Additionally, tracking physical and mental health indicators provides comprehensive insights into the overall wellbeing of the dog during training. Interaction with other trained military dogs allows for social conditioning, enabling dogs to acclimate to teamwork in diverse situations. Training sessions often incorporate group exercises, helping handlers realize how dogs perform both individually and within a unit. Achieving a high level of performance in both agility and discipline is paramount for operational success. Such assessments foster a culture of continuous improvement, ensuring that both handlers and dogs stay prepared to face the complexities of military operations. Therefore, a focus on ongoing assessment significantly enhances overall training efficiency and effectiveness.
The Role of Handlers in Agility Training
Handlers play an essential role in the agility training of military dogs, acting as the bridge between training concepts and practical applications. The bond formed between the handler and dog is vital to a successful training program; trust is the cornerstone of effective teamwork. Handlers must possess a deep understanding of canine behavior, learning styles, and effective communication methods that resonate with each individual dog. Consistent voice commands and body language are employed to create a clear communication pathway throughout training sessions. Handlers are responsible for maintaining motivation, providing rewards, and executing the training plan tailored for their dog. Additionally, handlers must stay attuned to signs of fatigue or stress in their dogs, adjusting sessions accordingly. The psychological aspect of training is equally important, as handlers must cultivate an environment that inspires confidence. A confident dog is more likely to take calculated risks during training exercises. This encourages the dog to perform optimally, even in high-pressure situations. Successful handlers not only inspire and motivate the dogs but also ensure that they remain focused and engaged throughout the agility training process to enhance performance.
Integrating agility training for military dogs with real-world tactical operations presents unique challenges and opportunities. As military operations become increasingly complex, training programs must adapt to ensure dogs are fully prepared. For example, training may involve simulating different terrains, such as urban, rural, or forest environments, allowing dogs to acclimate to varied conditions. Exposure to situational stress, noise distractions, and unpredictable movements enables dogs to develop advantageous instincts for real missions. Additionally, integrating technology like GPS and monitoring devices during training enhances safety and provides detailed insights into performance metrics. Military handlers and trainers are thus enabled to refine strategies based on data-driven evaluations collected in real-time. Flexibility in training allows for immediate recalibrations based on performance metrics, addressing any deficiencies noted. Including various scenarios in training programs assists in maintaining preparedness for sudden changes on the field. The role of military dogs, particularly during crisis situations, places immense responsibility on the training program’s effectiveness. Consequently, agility training can be regarded as a crucial component of a comprehensive military strategy. Tailored preparation ultimately equips military dogs and their handlers, fostering mutual understanding to fulfill critical operational needs.
Future Directions in Agility Training
The future of agility training for military dogs is set to evolve with advancements in technology and a deeper understanding of canine behavior. Emerging methodologies may incorporate virtual reality components, enhancing simulation environments. Such innovations enable handlers to experience and train their dogs in diverse scenarios without the need for physical setups. This level of training ensures flexibility and adaptability while evaluating performance under controlled conditions. Continued research into canine cognition can yield insights that reshape training paradigms, allowing for more refined approaches tailored to individual dogs. Genetic considerations may come into play as well, guiding selection processes for training programs. Moreover, interdisciplinary collaboration between veterinarians, behaviorists, and trainers can offer a more holistic approach to canine health and effectiveness in training. Regular updates on best practices will keep military protocols aligned with global trends in dog training methodologies. Implementing mixed-reality training sessions that blend physical and digital worlds helps create more engaging experiences for both dogs and handlers. This seamless fusion invites exploration into boundaries previously unimagined, ultimately enriching the effectiveness of military operations. Therefore, the trajectory of agility training stands poised for remarkable developments that align with the future of military dogs in tactical scenarios.
In conclusion, agility training for military dogs is not merely about physical capability; it encompasses a comprehensive understanding of the dog-handler dynamic. Emphasizing adaptability, coordination, and communication forms the foundation of effective training programs. As military demands continue to evolve, so too must the strategies employed in training. This dual focus on technique and technology offers opportunities to ensure operational readiness for all involved. Evaluating progress regularly and incorporating technological advancements paves the way for substantive improvements in training. Moreover, recognizing the immense value provided by military dogs reinforces their status as indispensable assets. Each successful mission underscores the benefits of rigorous agility training models, further justifying its inclusion in military programs across the globe. Beyond operational efficiency, such training fosters a gratifying bond between handlers and their dogs, leading to success in tense and high-pressure situations. As best practices develop in the coming years, both dogs and handlers will continue to benefit from innovations that optimize their training experiences. Ultimately, the role of agility training in military contexts emphasizes a profound commitment to excellence, safety, and mutual respect, establishing a strong foundation for future success in tactical operations.